2.9K
From how offices are designed to the way people work, modern workplaces are undergoing dramatic changes.
As a part of this shift in work culture, some organizations now allow employees to use their personal device for work. The Bring Your Own Device policy, as it is commonly known, is fast gaining popularity — especially with startups.
The global market for BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) and Enterprise Mobility is projected to be worth US$110.0 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to US$331.6 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.1% from 2023 to 2030.
So what are the pros and cons of allowing employees to bring their own devices?
In this article, we’ll discuss 10 BYOD pros and cons in detail. We’ll also talk about the best ways to implement a BYOD system at your workplace.
Table of Contents
Let’s jump right in.
10 BYOD pros and cons
Bring Your Own Device (acronym – BYOD) is the practice of letting employees use any personally owned device like laptop, mobile phone, tablet, etc., for office work.
They can use their personal smart devices to access the company information and work-related data instead of the company-issued ones.
The BYOD trend is now becoming a way of life for many employees. Intel first implemented it in 2009 but became increasingly popular after 2011 as more companies started implementing it.
Let’s explore five reasons behind this popularity:
A. 5 key BYOD pros
Here are five pros of BYOD and why some companies prefer a BYOD system:
1. Cost savings
Providing devices for all employees can significantly increase your overall costs, especially if you have a large organization. Additionally, not all employees may be comfortable or well versed with handling the devices you provide.
But having a BYOD policy can significantly reduce your expenses of:
- Purchasing or renting devices for each employee.
- Providing training for using new devices.
- Hiring hardware and IT support teams.
According to Cisco Internet Business Solutions Group, these savings add up to $3,150 per employee per year.
Additionally, when employees bring their own devices, they take better care of them and save you the additional cost of providing alternative devices.
2. Up-to-date technology
People may not update company-owned devices regularly. They may even choose to ignore any security updates, which may put your confidential data at risk.
However, they are likely to be more vigilant about keeping their personal laptops and other devices up-to-date and install the latest available updates.
Also, it may not be financially possible for an organization to keep purchasing new devices for all employees to keep up with the latest computer and mobile technology. But employees may often change their personal devices whenever newer versions are available.
When they use these devices for work, you’ll have faster, powerful, and modern devices that can work seamlessly without too many glitches.
3. No training required
Not all employees may be tech-savvy enough to quickly grasp a new Operating System (OS) or software.
For example, the older generation of employees may be used to the Windows OS. So if you provide devices with other OS like Linux, Mac OS, etc., they’ll have a more significant learning curve.
They’ll also require intensive training to familiarize themselves with even the basic functions of that system and device.
It’ll increase your training costs and also may cause employee resentment.
However, a BYOD arrangement allows employees to use the devices they’re most familiar and comfortable with, eliminating the need for any additional training.
4. A happier workforce
As an organization, you may want to bring in uniformity by allocating similar devices.
However, the current multigenerational workforce is quite particular regarding the smartphone and laptops they use.
While you may provide the best-suited gadget for work with cutting-edge technology, many employees may not be happy even with that.
A study by VMware found that 61% of the participants reported that they were happier in their jobs when they could use their personal device for work.
The BYOD system can enhance employee satisfaction since employees are already comfortable with their device — they can even customize the device according to their preferences.
5. Increased productivity
According to a study by the Social Market Foundation, happy and contented employees are up to 20% more productive than unhappy employees.
Additionally, in the BYOD model, people can bring the device they’re accustomed to and start being productive right away. It can boost employee morale and increase their engagement.
Satisfied employees can provide better customer service and enhance the customer experience, which can ultimately positively affect your bottom line.
Wondering how you can measure employee productivity?
Check out the 10 best team productivity tools that can help you out.

B. 5 major BYOD cons
While BYOD has its benefits, certain disadvantages of BYOD may not make it suitable for many companies.
Here are some of the major cons of Bring Your Own Device system:
1. Lack of uniformity in devices
A significant drawback of the BYOD model is the diversity of devices used for office work.
For example, some employees may prefer a Windows tablet and laptop, while others would be comfortable only with an iPad and a MacBook. Additionally, some may keep upgrading their smart devices every 2-3 years, while others may use the same device for many years.
Having multiple devices may lead to operational and compatibility issues with your company’s software. Your organization may be using a particular software for completing projects and tasks.
Since the devices are varied, employees may face difficulties while installing or using these programs. The software may not even work for older devices.
Additionally, the same software may have different shortcuts or versions for different OS. It may make it difficult for employees to collaborate on different devices, especially if they need to send files to each other and edit them.
As a result, you may have to create different directives, SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures), and information packets for all different types of devices used in your organization.
2. Increased distraction
Bringing any personal device to work means that social media apps, games, and other distractions can interfere with the employees’ productive hours.
As an employer, you may not be able to restrict these apps on the employee device.
However, you can track how much time an employee spends on these apps and websites using an employee productivity management tool like Time Doctor.
You can use Time Doctor to track how many hours an employee spends on a particular task or project. You can also monitor whether they access any non-work apps and websites during work hours.
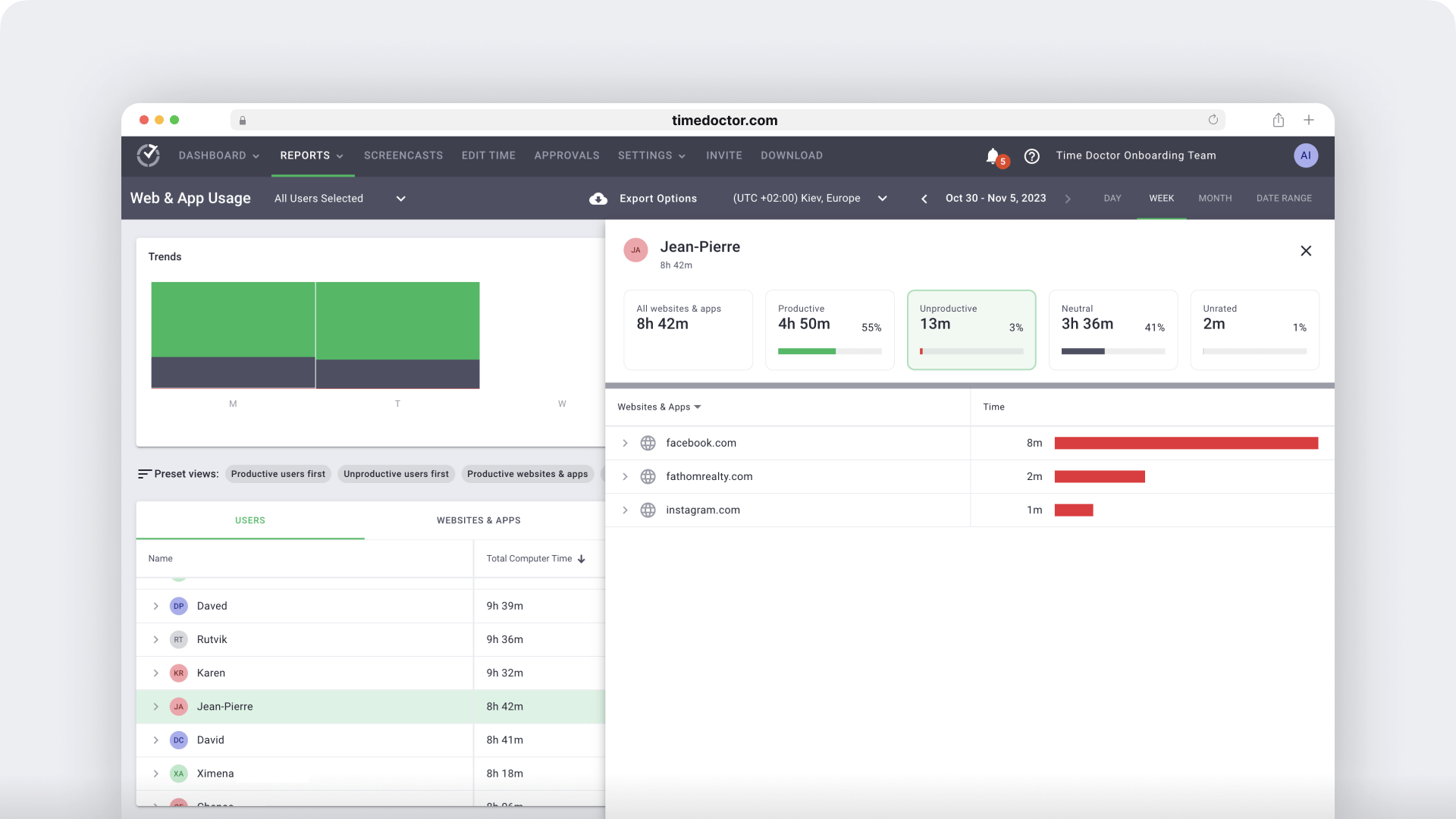
Learn more about Time Doctor’s other beneficial features.
3. Higher security risk
When employees use their own device for work, they’re likely to carry it back and forth between their home and office. It can significantly increase the risk of theft or misplacement.
According to a data breach analysis, 41% of all data breaches during 2005-2015 have mainly been due to lost devices.
Also, you may not have much control over who uses the employee’s personal devices when they’re not at work. Children may mistakenly download risky apps or software and jeopardize the entire device, including your company’s confidential information.
There’s also a risk that the employee may intentionally or unintentionally leak trade secrets or other classified information to hackers while using unsecured WiFi connections.
But you can take security measures to provide some level of protection to personal devices. These include:
- Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM): A set of policies, technologies, and processes that secure and manage all mobile devices (Android, iPhone, etc.) within an organization.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM): A third-party security software that allows IT departments to manage, monitor, and secure any mobile device, like a smartphone, tablet, and laptop.
- Mobile Application Management (MAM): Software and services that control access to internal and commercial applications used for work purposes.
4. Difficult data retrieval
Corporate data retrieval may become difficult in emergency situations when employees use their personal devices for company work.
How?
In a BYOD program, it becomes necessary to remove the company’s confidential data from all devices when the employee leaves your company. However, accessing personal devices may be a challenge since some employees may consider it an invasion of privacy.
In cases of absconding employees, this may become an even more strenuous task.
You will need to ensure that your IT team can remotely access all employee devices to quickly retrieve the company’s data in these emergencies.
5. Legal issues
There are various legal, privacy, and security concerns that may arise after implementing a BYOD system.
Employees, especially new hires, may not fully understand the correct practices that they should follow while using their personal devices for work.
That’s why you should have a detailed BYOD policy in place. Certain issues like retaining, sharing, accessing, and deleting the corporate data need to be addressed clearly in the policy.
You should also indicate the implications of accessing company data after work hours or the misuse of this information.

6 best practices for implementing BYOD at your workplace
Despite the challenges, there’s undoubtedly a growing trend for adopting a BYOD model.
If you’re keen on implementing this system in your organization, there are a few ways to overcome the cons and make it successful.
Let’s look at the six best ways to set up a BYOD arrangement:
1. Decide whether BYOD is right for your company
First, analyze the pros and cons of BYOD and consider your company’s nature of work to understand whether it’s okay to allow your employees to use their devices for work purposes.
For example, if your company is into research or security solutions, you may not want to risk implementing a BYOD system.
2. Create a comprehensive BYOD policy
After deciding to allow employees to bring their devices, you need to create a comprehensive BYOD policy that details all the rules.
Your policy should cover:
- Who’s eligible for the policy.
- Which devices are permitted access to your company network.
- Which apps are allowed and which are blacklisted.
- The minimum processing power, memory storage, and other requirements of the personal device.
- Who owns the company information stored on the employee’s device.
- The security rules and legal constraints.
And any other points that may apply to your particular industry.
3. Secure company’s data
In order to prevent a security breach, you need to adopt a multi-faceted approach.
All employees must install a specialized app that has two-factor authentication for accessing the company data.
You should also arrange for annual training programs on cybersecurity to update your employees regarding any security threat or scam and the proper ways to deal with them.
4. Protect employee’s personal data
Another major concern about using personal devices for work purposes is that employees may feel an invasion of privacy when you monitor their devices.
You should ensure that your device management software doesn’t monitor any employee’s personal data. Also, it shouldn’t access any personal app or copy or store the employee’s personal information.
5. Plan for emergencies
In emergency situations like loss or theft of a device, absconding employee, etc., you should be able to quickly remove any corporate data from the said device.
The only way to do that is remotely wiping off the data. An EMM solution can allow you to do that.
Additionally, in case of misplaced devices, your employees should know whom to report the incident to and the entire process of recording the incident.
You should also have an exit BYOD strategy for such devices or for those that new ones will replace.
6. Ensure continuous compliance
Finally, it’s important to remember that making a BYOD policy isn’t a one-time thing. It’s a continuous process, and you should review it regularly.
You need to review the three critical factors:
- Policy compliance
- Data usage
- Security measures
The main aim of these evaluations is to understand whether all employees are adhering to the policy or not.
If there are any discrepancies, regular assessments can allow you to reach out to those employees and remind them about their responsibilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about BYOD
1. What is BYOD, and how does it work in the workplace?
Answer: BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) is a policy where employees use their personal devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets, to access company resources, systems, and data for work purposes. This policy allows employees to work with devices they are familiar with and may reduce the need for businesses to supply devices for every employee. However, it also requires security protocols, such as encryption and data management policies, to protect sensitive company information on personal devices.
2. Is BYOD safe for my company’s data?
Answer: While BYOD offers convenience, it can present significant security risks if not managed properly. Employees’ personal devices may not always have the same level of security as company-issued hardware. To mitigate these risks, companies should implement security measures such as Mobile Device Management (MDM), Virtual Private Networks (VPN), two-factor authentication, and data encryption. Additionally, regular security training for employees on the dangers of unsecured WiFi and phishing attacks can help minimize risks.
3. What legal issues should I consider before implementing a BYOD policy?
Answer: Legal issues surrounding BYOD often revolve around data privacy and ownership. Companies need to clearly define the following in their BYOD policies:
- Ownership of company data stored on personal devices.
- Procedures for wiping corporate data when an employee leaves the company or if a device is lost.
- Policies for accessing employee devices for security monitoring, which must respect local privacy laws such as GDPR or CCPA.
- Guidelines regarding after-hours access to company data to avoid potential overtime wage claims.
Consulting with a legal expert to create a compliant BYOD policy is highly recommended.
4. What kind of devices can be used in a BYOD policy?
Answer: The types of devices allowed in a BYOD policy can vary depending on the company’s needs and security requirements. Generally, companies allow employees to use smartphones, laptops, and tablets. However, organizations may restrict the use of certain operating systems or older models that don’t meet security or performance standards. The BYOD policy should outline the minimum specifications, such as the operating system version, storage capacity, and required security features (like encryption) for any device used for work.
5. What happens if an employee’s device is lost or stolen?
Answer: In the event of a lost or stolen device, companies should have procedures in place to protect sensitive data. This often includes:
- The ability to remotely wipe corporate data from the lost device.
- Immediate reporting procedures that employees must follow to notify IT or HR departments.
- Preventive measures like requiring employees to use device encryption and strong passwords, making it harder for unauthorized individuals to access company data.
Using Mobile Device Management (MDM) tools can streamline this process and offer more control over company data on personal devices.
6. Can employees opt-out of the BYOD policy?
Answer: Yes, employees can opt out of BYOD programs in many companies. In such cases, the employer must provide company-owned devices for work purposes. It’s essential to have an opt-out clause in the BYOD policy so that employees who don’t feel comfortable using their personal devices for work still have the tools necessary to perform their duties effectively.
9. How does BYOD affect employee productivity?
Answer: BYOD can enhance employee productivity as it allows employees to use devices they are familiar and comfortable with, reducing the learning curve for new hardware or software. Studies suggest that BYOD can increase productivity by up to 20% since employees tend to be more engaged when working on devices they prefer. However, it can also introduce distractions if employees use personal apps during work hours, which can be mitigated by time-tracking and productivity tools.
Final thoughts
BYOD has its pros and cons. You must weigh both sides before deciding whether to implement it in your company.
If your company has multiple departments with varied work, it may be challenging to keep track of all personal devices and protect your sensitive information.
On the other hand, if you have a startup or a small business and don’t have a dedicated IT department, a BYOD agreement can significantly reduce your costs.
Use the information we covered here as a guideline to decide whether BYOD is right for your business or not.

Liam Martin is a serial entrepreneur, co-founder of Time Doctor, Staff.com, and the Running Remote Conference, and author of the Wall Street Journal bestseller, “Running Remote.” He advocates for remote work and helps businesses optimize their remote teams.


